Conventional Ethernet is lossy in nature, which means that frames might be dropped or lost under congestion conditions. Therefore, Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) provides a new specification to the existing Ethernet standard. It eliminates the lossy nature of Ethernet and enables convergence of various types of network traffic on a common Ethernet infrastructure.
CEE eliminates the dropping of frames due to congestion and thereby ensures lossless transmission of FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) traffic over an Ethernet network. The lossless Ethernet is required for the reliable transmission of FC data over an Ethernet network.
Also Read: FCoE Architecture
Also Read: FCoE Architecture
Unlike TCP/IP, the loss of a single FC frame typically requires the entire FC exchange to be aborted and re‐transmitted, instead of just re‐sending a particular missing frame. CEE makes a high-speed (such as 10 Gbps or higher) Ethernet network a viable storage networking option, similar to an FC SAN.
Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) Functions
The CEE requires certain functionalities. These functionalities are defined and maintained by the Data Center Bridging (DCB) task group, which is a part of the IEEE 802.1 working group. These functionalities are
- Priority-based flow control
- Enhanced transmission selection
- Congestion notification
- Data center bridging exchange protocol
Priority based Flow Control (PFC)
Traditional FC manages congestion through the use of a link-level, credit-based flow control that guarantees no loss of FC frames. Typical Ethernet, coupled with TCP/IP, uses a packet drop flow control mechanism. The packet drop flow control is not lossless. This challenge is eliminated by using an IEEE 802.3x Ethernet PAUSE control frame to create a lossless Ethernet.
A receiver can send a PAUSE request to a sender when the receiver’s buffer is filling up. Upon receiving a PAUSE frame, the sender stops transmitting frames, which guarantees no loss of frames. The downside of using the Ethernet PAUSE frame is that it operates on the entire link, which might be carrying multiple traffic flows.
A receiver can send a PAUSE request to a sender when the receiver’s buffer is filling up. Upon receiving a PAUSE frame, the sender stops transmitting frames, which guarantees no loss of frames. The downside of using the Ethernet PAUSE frame is that it operates on the entire link, which might be carrying multiple traffic flows.
- PFC provides a link-level flow control mechanism. PFC creates eight separate virtual links on a single physical link and allows any of these links to be paused and restarted independently.
- PFC enables the PAUSE mechanism based on user priorities or classes of service. Enabling the PAUSE based on priority allows creating lossless links for network traffic, such as FCoE traffic.
- This PAUSE mechanism is typically implemented for FCoE while regular TCP/IP traffic continues to drop frames.
Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS)
Enhanced transmission selection (ETS) provides a common management framework for the allocation of bandwidth to different traffic classes, such as LAN, SAN, and Inter Process Communication (IPC). For example, an administrator may assign 40 percent of network bandwidth to LAN traffic, 40 percent of bandwidth to SAN traffic, and 20 percent of bandwidth to IPC traffic. When a particular class of traffic does not use its allocated bandwidth, ETS enables other traffic classes to use the available bandwidth.
Also Read: Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) SAN Introduction
Also Read: Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) SAN Introduction
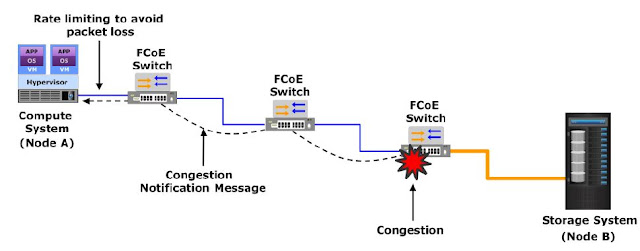
Congestion notification (CN)
Congestion notification (CN) provides end-to-end congestion management for protocols, such as FCoE, that do not have built-in congestion control mechanisms. Link level congestion notification provides a mechanism for detecting congestion and notifying the source to move the traffic flow away from the congested links. Link level congestion notification enables a switch to send a signal to other ports that need to stop or slow down their transmissions.
DCBX is a discovery and capability exchange protocol, which helps CEE devices to convey and configure their features with the other CEE devices in the network. DCBX is used to negotiate capabilities between the switches and the network adapters, which allows the switch to distribute the configuration values to all the attached adapters. This helps to ensure consistent configuration across the entire network.
Previous: 6.1 The need for a Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) Network
Go To >> Index Page
Previous: 6.1 The need for a Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) Network
Go To >> Index Page
What Others are Reading Now...


0 Comment to "6.2 Functions of Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) "
Post a Comment