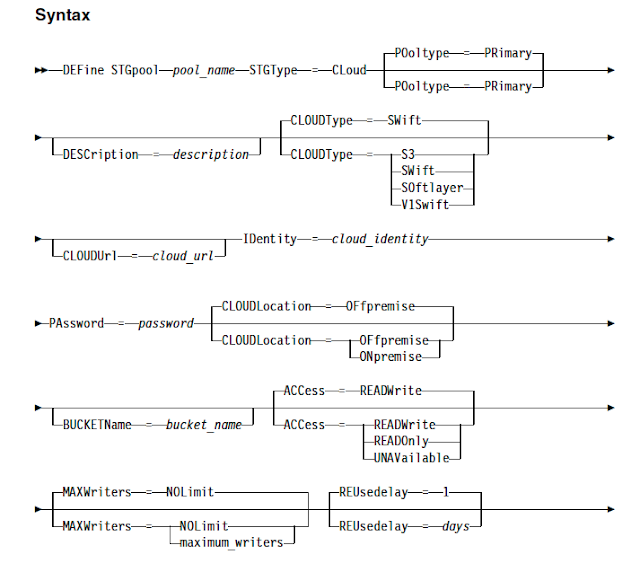
Since IBM now supports various cloud storage services to take the backups, you can use cloud container storagepools to store both the deduplicated data and non-deduplicated data and restore the data as required. Starting from IBM Spectrum Protect (TSM) V 7.1.7, you can configure cloud-container storage pools on 4 of the popular and widely used cloud based object storage systems to backup the data. However, the backup performance of a cloud-container storage pool largely depends on the network connections between the server and the cloud. Sending data to cloud storage requires good network bandwidth along with the advanced security features. But most of the small and medium sized organisations cannot afford to buy the high network bandwidths if they want to use cloud as the storagepool destinations.
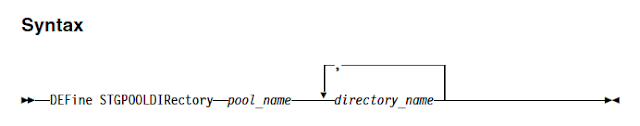
To address this situation, IBM has introduced a new hybrid and optimised data transfer techniques. You can now define local storagepool directory by using the new DEFine STGPOOLDIRectory command where the data is stored temporarily before it is transferred to the cloud. This technique is generally referred as hybrid cloud backup. This hybrid cloud backup feature will help you to set up local storage for data that is later moved to the cloud. By assigning one or more local storage directories to a cloud-container storage pool, you can enhance the performance of backup operations to the cloud. When you back up the data to local storage, the data is buffered efficiently into disk containers and moved to the cloud as larger objects. With larger objects, you can achieve better performance results. Use this command to define one or more directories in a directory-container or cloud-container storage pool.
For Example: define stgpooldirectory pool1 /storage/dir1,/storage/dir2
When you define a local storage directory, data is temporarily stored in the directory during data ingestion, and is then moved to the cloud. you can set up local storage for data that is later moved to the cloud. By assigning a local storage directory to a cloud-container storage pool, you can enhance the backup performance of small objects, for example, client-transaction data.
After you define a cloud-container storage pool, create one or more directories that are used for local storage. You can temporarily store data in local storage during the data ingestion, before the data is moved to the cloud. In this way, you can improve system performance.
Watch the below video on how to configure cloud services to configure hybrid cloud backups in 3 simple steps by using IBM Spectrum Protect and Amazon S3.
Watch the below video on how to configure cloud services to configure hybrid cloud backups in 3 simple steps by using IBM Spectrum Protect and Amazon S3.