In today's data center environment, we generally have at least two major networks - Ethernet network and Fibre Channel network. Ethernet is used for transferring regular management traffic and Fibre Channel is used for transferring storage traffic.
Ethernet is the commonly used network in all types of data centers because of its versatility and scalability. Most data centers deploy one or more ethernet networks because of its advantages. However, ethernet networks are not good in performance particularly latency and the recently evolved 10G and 40G Ethernet technologies have tried to address these performance issues. Ethernet is also well known for its dropping frames during congestion, for example when a switch is receiving frames but can’t forward them yet because the next hop is busy. When packet loss like this happens, it’s the job of protocols higher in the network stack, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), to take care of re-transmitting frames that never reach their destination.
Also Read: Overview of Fibre Channel (FC) SAN Protocol
Also Read: Overview of Fibre Channel (FC) SAN Protocol
On the other hand, Fibre Channel (FC) networks are high speed, low latency networks that are commonly used for transporting storage traffic. Unlike ethernet, FC is a lossless technology which doesn't drop packets during congestion. This combination of low latency and lossless capability makes this FC technology ideal for transporting SCSI traffic. However, FC networks are less versatile and less scalable and expensive than Ethernet networks. So the main goal of FC technology is to provide high performance, low overhead interconnects and whereas the main goal of ethernet network technology is to provide versatility and scalability.
Why Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) ?
So the Converged Data Center network idea consolidates Ethernet and fibre channel technologies to provide rationalised and consolidated cost effective infrastructure for data transfers. The main goal of this converged data center networks are
- To reduce the number of network adapters in physical servers
- To reduce the number of cables coming out of each physical server
- To reduce the number of switches in the infrastructure
So instead of having one set of network adapters, cables, and switches dedicated to Fibre Channel and another set of adapters, cables, and switches dedicated to Ethernet, with a converged network we have only a single set of network adapters, cables, and switches and run our Ethernet and FC storage traffic over them.
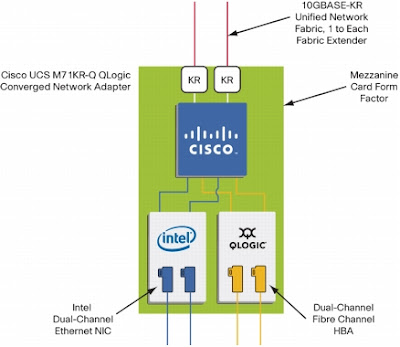
Need for an enhanced Network Adapters - Converged Network Adapter (CNA)
Traditional Ethernet networks are accessed via a network adapter called a network interface
card (NIC). Each host that wants to connect to the Ethernet network needs at least one. Conversely, traditional Fibre Channel networks are accessed via a network adapter called a host bus adapter (HBA) in each host.
However, to create a single data center network capable of transporting IP and FC storage traffic, Ethernet adapters had to be significantly enhanced and upgraded. So, ideally to set up a new server in the data center, we need a new type of advanced adapter known as Converged Network Adapter (CNA) in it, and you can do all the networking you want.
Accessing an FCoE network requires a new type of network adapter called a converged network adapter (CNA). All three of these network adapter cards are implemented as PCI adapter cards. They can be either expansion cards or directly on the motherboard of a server in what is known as LAN on motherboard (LOM).
Also Read: FCoE Connectivity Models
A CNA is exactly what the name suggests - a NIC and an HBA converged into a single network card. For performance reasons, CNAs provide NIC and HBA functionality in
hardware (usually an ASIC) so that things like FCoE encapsulation can be fast without impacting host CPU resources.
You can do general purpose IP networking, FC storage networking, iSCSI storage, NAS, maybe even low-latency, high-performance computing. A single network adapter and a single cable will do all the job. It also has the positive effect of reduced power and cooling costs. All in all, it delivers reduced data center running costs and lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
card (NIC). Each host that wants to connect to the Ethernet network needs at least one. Conversely, traditional Fibre Channel networks are accessed via a network adapter called a host bus adapter (HBA) in each host.
However, to create a single data center network capable of transporting IP and FC storage traffic, Ethernet adapters had to be significantly enhanced and upgraded. So, ideally to set up a new server in the data center, we need a new type of advanced adapter known as Converged Network Adapter (CNA) in it, and you can do all the networking you want.
Accessing an FCoE network requires a new type of network adapter called a converged network adapter (CNA). All three of these network adapter cards are implemented as PCI adapter cards. They can be either expansion cards or directly on the motherboard of a server in what is known as LAN on motherboard (LOM).
Also Read: FCoE Connectivity Models
A CNA is exactly what the name suggests - a NIC and an HBA converged into a single network card. For performance reasons, CNAs provide NIC and HBA functionality in
hardware (usually an ASIC) so that things like FCoE encapsulation can be fast without impacting host CPU resources.
You can do general purpose IP networking, FC storage networking, iSCSI storage, NAS, maybe even low-latency, high-performance computing. A single network adapter and a single cable will do all the job. It also has the positive effect of reduced power and cooling costs. All in all, it delivers reduced data center running costs and lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
So to create this new enhanced Ethernet, the IEEE formed a new task group within the 802.1 working group called as Data Center Bridging (DCB). This DCB is responsible for the development of a data center ethernet network that is capable of transporting all common data center network traffic types like IP LAN traffic, FC storage traffic and infiband high performance computing traffic. So the enhanced ethernet generally called as either Data Center Bridging (DCB) or Converged Ethernet (CEE) or Data Center Fabric or Unified Fabric.
- Increased bandwidth
- Classes of service
- Priorities
- Congestion management
- Enhanced transmission selection (ETS)
All these enhancements can be obtained by using Converged network adapters and a whole load of new hardware requirements such as cables, switch ports, and switches.
Previous: 5.5 Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) SAN Introduction
Go To >> Index Page
Previous: 5.5 Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) SAN Introduction
Go To >> Index Page
What Others are Reading Now...


0 Comment to "6.1 The need for a Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) Network "
Post a Comment