IBM has introduced new set of commands to easily repair the damaged data on the directory-container storage pool on both source and target TSM servers when you enable replication techniques. By using these commands you can save lots of time and money which we spend on recovering the damaged storage pools earlier. You can use PROTECT STGPOOL, AUDIT CONTAINER and REPAIR STGPOOL commands to repair the damaged data on the directory-container storage pool on the target TSM servers.
The repairing process of the directory-container storage pool on the target server is done automatically by using the above commands. If the damaged data extent was backed up on a directory-container storage pool on the target server, you can repair the data extent manually by using the REPAIR STGPOOL command. Information about what is repaired is recorded in the activity log for the target server. However, the automatic repair process has the following limitations:
- Both the source server and the target server must be at V7.1.5 or later.
- To be repaired, extents must already be marked as damaged on the target server. The repair process does not run an audit process to identify damage.
- Only target extents that match source extents are repaired. Target extents that are damaged but have no match on the source server are not repaired.
- Extents that belong to objects that were encrypted are not repaired.
- The timing of the occurrence of damage on the target storage pool and the sequence of REPLICATE NODE and PROTECT STGPOOL commands can affect whether the repair process is successful. Some extents that were stored in the target storage pool by a REPLICATE NODE command might not be repaired.
So to repair the damaged data, you need to first find out what is the damaged data in the target storage pool. To identify the damaged data, we use AUDIT CONTAINER command and QUERY DAMAGED commands. The AUDIT CONTAINER command is used to scan for inconsistencies between database information and a container in a directory-container storage pool. Whereas QUERY DAMAGED command is used to display information about damaged data extents in a directory-container or cloud-container storage pool. Use this command together with the AUDIT CONTAINER command to determine a recovery method for the damaged data.
Steps to follow to repair damaged data on the directory-container storage pool on the Target server
Step 1: Verify the consistency of database information for a directory-container on the target TSM server
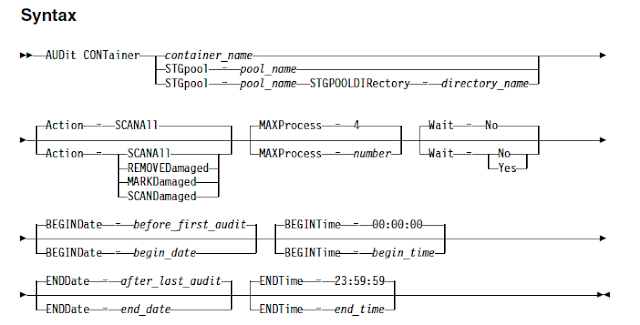
Use AUDIT CONTAINER command to scan for inconsistencies between database information and a container in a directory-container storage pool. You can use this command to complete the following actions for a container in a directory-container storage pool
- Scan the contents of a container to validate the integrity of the data extents
- Remove damaged data from a container
- Mark an entire container as damaged
audit container stgpool=prdpool maxprocess=5 action=markdamaged
Also you can specify the type of action to be performed when using this command by using Action parameter. It specifies what action the server takes when a container in a directory-container storage pool is audited. It has the following options
SCANAll - Specifies that the server identifies database records that refer to data extents with inconsistencies. This value is the default. The server marks the data extent as damaged in the database.
REMOVEDamaged - Specifies that the server removes any files from the database that reference the damaged data extent.
MARKDamaged - Specifies that the server explicitly marks all data extents in the container as damaged.
Also Read: DISK vs FILE device classes performance
If the audit does not detect an error with a data extent that is marked as damaged, the state of the data extent is reset. The data extent can then be used. This condition provides a means for resetting the state of damaged data extents if errors are caused by a correctable problem. The SCANALL and SCANDAMAGED options are the only options that reset a damaged extent if it is found not to be damaged.
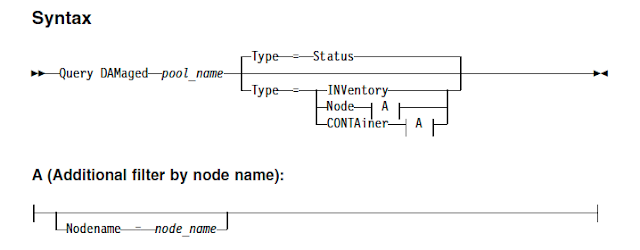
Use QUERY DAMAGED command to display information about damaged data extents in a directory-container or cloud-container storage pool. Using this command together with the AUDIT CONTAINER command will help you to determine a recovery method for the damaged data.
For example, to display status information about damaged or orphaned data extents
query damaged prdpool type=status
Storage Pool Non-Deduplicated Deduplicated Cloud Orphaned Name Extent Count Extent Count Extent Count --------------- ------------- ---------- -------------POOL1 65 238 18
Use the Type parameter to specify the type of information to display. You can use the following options
Status - Specifies that information is displayed about damaged data extents. For cloud storage pools, orphaned extents are also displayed. This is the default.
Node Specifies that information about the number of damaged files per node is displayed.
INVentory - Specifies that inventory information for each damaged file is displayed.
CONTAiner - Specifies that the containers that contain damaged data extents or cloud orphaned extents are displayed. For directory-container storage pools, storage pool directories are also displayed.
Nodename - Specifies that damaged file information for a single node is displayed.
Step 3: Automatic Repair of damaged extents
Starting from Tivoli Storage Manager Version 7.1.5, when a storage pool protection process runs for a directory-container storage pool on a source server, damaged extents in the target server's storage pool are repaired automatically.
You can check the information about what is repaired is recorded in the activity log for the target server once the storage pool protection process gets completed. Ideally it is recommended to schedule the step 2 and step 3 in regular intervals so that the damaged data extents are automatically repaired during daily storagepool protection process.

Very nice article. Thanks for sharing information on data protection disaster recovery replication.
ReplyDelete