Data is stored and accessed by applications using the underlying storage infrastructure. The key components of this infrastructure are the OS (or file system), connectivity, and storage. The server controller card accesses the storage devices using predefined protocols, such as IDE/ATA, SCSI, or Fibre Channel (FC) as discussed in earlier posts.
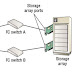
IDE/ATA and SCSI are popularly used in small and personal computing environments for accessing internal storage. FC and iSCSI protocols are used for accessing data from an external storage device (or subsystems). External storage devices can be connected to the servers directly or through the storage network. When the storage is connected directly to the servers, it is referred as Direct-Attached Storage (DAS).
By using the above SAN features and protocols data which is stored in the storage systems can be accessed by various methods. The overview of these methods are discussed below. Detail description will be in the next posts.
By using the above SAN features and protocols data which is stored in the storage systems can be accessed by various methods. The overview of these methods are discussed below. Detail description will be in the next posts.
Data Access Methods from Storage Systems
Data can be accessed over a storage network in one of the following ways
- Block Level
- File Level
- Object Level
- User component
- Storage component.
The file system maps the file attributes to the logical block address of the data and sends the request to the storage device. The storage device converts the logical block address (LBA) to a cylinder-head-sector (CHS) address and fetches the data.
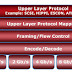
Depending on the type of the data access method used for a storage system, the controller can either be classified as block-based, file-based, object-based, or unified. An intelligent storage system can have all hard disk drives, all solid state drives, or a combination of both. The different types of data access methods are shown in the below figure.
In a block-level access, the file system is created on a server, and data is accessed on a network at the block level. In this case, raw disks or logical volumes are assigned to the servers for creating the file system.
Also Read: Importance of Cache technique in Block Based Storage Systems
Also Read: Importance of Cache technique in Block Based Storage Systems
In a file-level access, the file system is created on a separate file server or at the storage side, and the file-level request is sent over a network. Because data is accessed at the file level, this method has higher overhead, as compared to the data accessed at the block level.
Also Read: Overview of NAS Arrays
Also Read: Overview of NAS Arrays
Object-level access is an intelligent evolution, whereby data is accessed over a network in terms of self-contained objects with a unique object identifier. In this type of access, the file system’s user component resides on the server and the storage component resides on the storage system. This type of data access method is mainly used for offering emerging technologies like cloud and big data.
Also Read: Key Features of Object Based Storage Systems
Previous: 2.6 What are Intelligent Storage Systems ?
Also Read: Key Features of Object Based Storage Systems
Previous: 2.6 What are Intelligent Storage Systems ?
Go To >> Index Page
What Others are Reading Now...






0 Comment to " 2.7 Accessing data from the Intelligent Storage Systems"
Post a Comment